The intelligent flight modes of the DJI Mini 3 Pro are Active Track, Spotlight, and Point of Interest. They are grouped under the name Focus Track. These modes are used to easily and precisely achieve all kinds of cinematic moves. They are also used for tracking moving targets
One of the most important upgrades of the Mini 3 Pro compared to the Mini 2 is the availability of intelligent flight modes
I have done specific articles for each intelligent mode of Focus Track
Other interesting related articles you might want to watch
- Master Shots with the Mini 3 Pro
- Quick Shots with the Mini 3 Pro
- 9 drone moves for stunning cinematic video
- Mini 3 Pro camera settings for video
Settings
The settings are the same for the three intelligent flight modes
They can be used with both color modes of the Mini 3, Normal and D Cinelike, which is very handy. They can also be used for vertical footage
Unfortunately, Focus Track is only available at frame rates of up to 30 frames per second, which is a bit disappointing, as we cannot apply real slowdown when tracking, which would be useful for filming action or sport
Focus Track and obstacle avoidance
Tracking is closely related to the ability to avoid obstacles
A fundamental upgrade of the Mini 3 compared to the Mini 2 is the presence of obstacle sensors. It is a tridimensional system with pairs of sensors on the front, back, and bottom. It is not omnidirectional like in the Mavic 3, as there are no sensors on the sides and top
For this reason, I recommend using the Mini 3 for close tracking only in areas without any obstacles. I would not use it in wooded areas. When tracking action or sports events I keep the aircraft well above obstacles
Here is my in-depth analysis of the obstacle avoidance system in the Mini 3 Pro. More details about the importance of the obstacle avoidance system in this other article article



How to Access the Intelligent Flight Modes
The interface for Focus Track is straightforward to use and much faster compared to previous models
To access Focus Track draw a rectangle around the target, a window appears at the bottom of the screen with the three intelligent flight modes
For moving targets, select the option Subject Scanning in the Control tab of the settings. A plus sign will appear on available targets. To select a target touch the plus sign
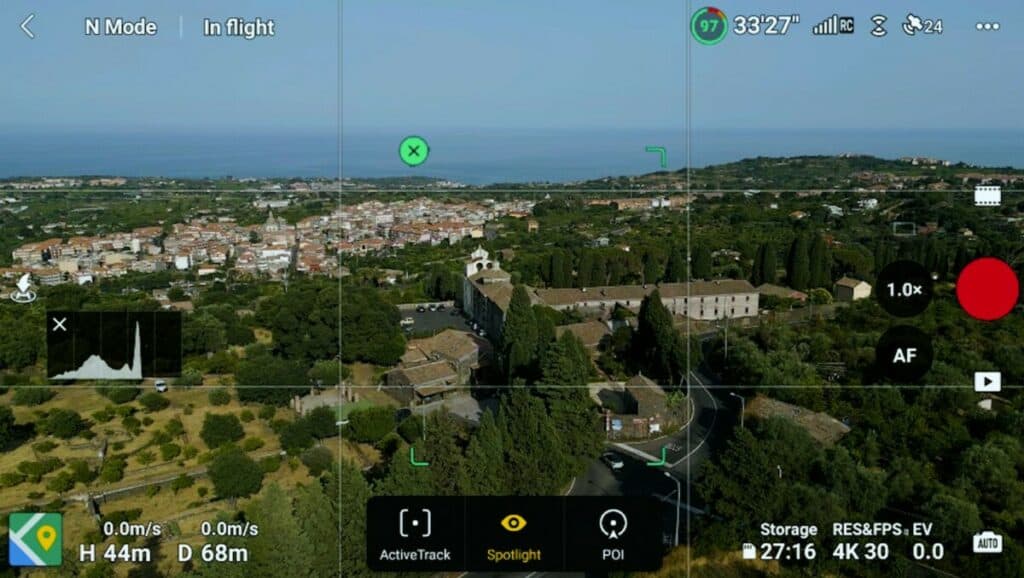

How to Use Active Track
All three intelligent flight modes of Focus Track have some tracking capability. The two modes used the most for tracking are Active Track and Spotlight
Active Track is the mode used primarily for autonomous tracking, in other words, to follow a moving target without an operator controlling the aircraft. For example, while walking, driving, or cycling not using the remote control
The tracking interface is not as advanced as the one of the Mavic 3, in which we can set 8 different positions compared to the target to the target. With the Mini 3, we have the choice between Trace and Parallel
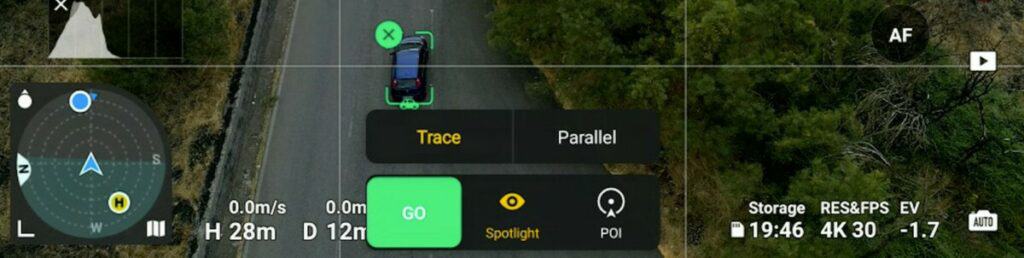
How to Use Trace Mode in Active Track
When using the option Trace of Active Track, the aircraft will follow the movement of the target at a constant distance from behind or in front of it. It is also possible to position the drone over the target with the camera facing down for top-down tracking
Choose a scene with no obstacles, such as a beach or a place with an interesting background. Tracking from behind works very well, even when the target changes direction. It is often more interesting to have the drone in front of the subject to follow, perhaps someone talking or singing, or two or more people discussing as they walk
The Mini 3 is able to track much closer to the ground compared to previous models, even less than one meter
How to Use Parallel Mode in Active Track
In Parallel mode within Active Track, the drone maintains constant height and distance from the target but follows laterally at an angle greater than 90 degrees to facilitate obstacle detection. This mode must be used very carefully and only in areas without obstacles, due to the lack of side sensors
The drone maintains control of the target even when it is covered by obstacles for a few seconds
Vertical video is an important feature of the Mini 3 and the ability to track in this format is a significant selling point for active users on social platforms
While tracking we can apply a progressive zoom using the right wheel of the remote control. This is useful for getting closer to the target, as we often have to keep the drone at a distance to stay above obstacles
How to Use Spotlight Intelligent Flight Mode
Spotlight Mode with Static Targets
Of the three modes, the one I use the most is probably Spotlight. It can be used in two different ways: with static targets and to track moving subjects
When using Spotlight mode with a static target, the subject will be kept in the same position in the frame regardless of the movements made by the drone. In other words, the camera is disconnected from the direction of the flight
A classic way of using Spotlight is to fly diagonally to the target to reveal the background thus creating a parallax effect, in this case revealing Mount Etna behind the monastery in the foreground
Here the camera is fixed on this lighthouse in a bay, while the drone makes a movement that reveals the Etna in the background
Spotlight is also very useful for real estate videography, to show the surroundings of a property
A well-known movement, very difficult to make manually, is the famous crane shot. The aircraft starts at a low altitude with the camera fixed on the target, then rises in altitude as it approaches until it is above the target for a bird’s eye view
With previous models, some movements could only be made by creating missions with a mode named Waypoints, a feature that sadly is no longer available in the models of the current DJI lineup. We can obtain very similar results using Spotlight, as we can control all the movements of the aircraft while maintaining the target in the center of the frame
Spotlight for Tracking
Using Spotlight mode is the best way to track when an operator controls the Mini 3
With Spotlight mode, if the target is a moving subject with the drone hovering, the camera will rotate to keep it in the frame. This is useful for following subjects moving in a confined space. Spotlight mode is also used for dynamic tracking, keeping the target in the center of the frame while the aircraft moves in any direction
Point of Interest Mode
How to Access Point of Interest Mode
As usual, we start by drawing a rectangle around the target to summon the small window with the three intelligent flight modes of Focus Track
When selecting Point of Interest a yellow arrow appears to choose the flight direction and speed. The aircraft will rotate around the target. We can use the two sticks of the remote controller to modify the height and the distance from the target, which adds considerable interest to cinematic movements
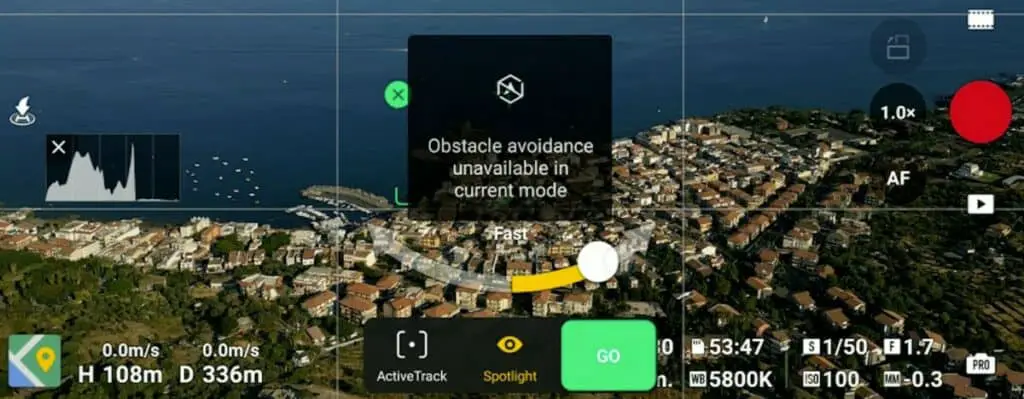
The rotational motion exposes the lack of side obstacle sensors in the Mini 2. Special care is needed to make sure to fly in a large open area or stay well above any obstacles
How to Use Point of Interest Mode
Rotating around a target is a very interesting way to reveal a scene, particularly when there are elements at different distances in order to create a parallax effect, with the different layers moving at different speeds according to the distance
By adding more movements we can make things more interesting. For example, here we have a seaside village in Sicily. A very simple way to show it is to simply advance towards the village at regular speed. The result is not bad, but we don’t know much about the context and the surroundings
We can change the angle and move forward again, but this time showing two other villages up ahead, with beautiful bays and volcanic islets, more interesting
Now let’s use Point of Interest in the simplest way. By simply turning counterclockwise, with the castle as the target, the scene becomes much more interesting because we add an element of surprise
We can make things more dynamic by adding movement with the two sticks on the remote control. In this case, I push the right stick to the right to move away from the target and to widen the view during the rotation, at the same time I go down slightly to better position the other two villages in the frame
In this other example, I use Point Of Interest with the camera pointed down, with the drone almost above the target. Descending and turning we achieve two well-known movements in cinematography: the screwdriver and the crane, for a fascinating result
